The company believes the hackers used an exploit published in July 2019 on GitHub by OpenZeppelin, a company that performs security audits...
 |
| The company believes the hackers used an exploit published in July 2019 on GitHub by OpenZeppelin, a company that performs security audits for cryptocurrency platforms. |
According to investigators, hackers appear to have chained together bugs and legitimate features from different blockchain technologies to orchestrate a sophisticated "reentrancy attack."
Reentrancy attacks allow hackers to withdraw funds repeatedly, in a loop, before the original transaction is approved or declined. The similarities between Uniswap and Lendf.me is that both platforms were using:
- Lendf.me protocol -- a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol developed by the dForce Foundation to support lending operations on the Ethereum platform.
- imBTC -- a token (coin) that runs on the Ethereum platform and is valued at a 1:1 rate with the Bitcoin cryptocurrency.
- ERC-777 -- one of the underlying technologies of the Ethereum blockchain meant to support smart contracts (both Lendf.me and imBTC run as smart contracts on the Ethereum platform).
"The ERC-777 token standard has - to our knowledge - no security vulnerabilities," said Tokenlon, the company behind imBTC. "However, the combination of using ERC777 tokens and Uniswap/Lendf.Me contracts enables [...] reentrancy attacks," the company wrote in a post-mortem report of the Uniswap and Lendf.me attacks.
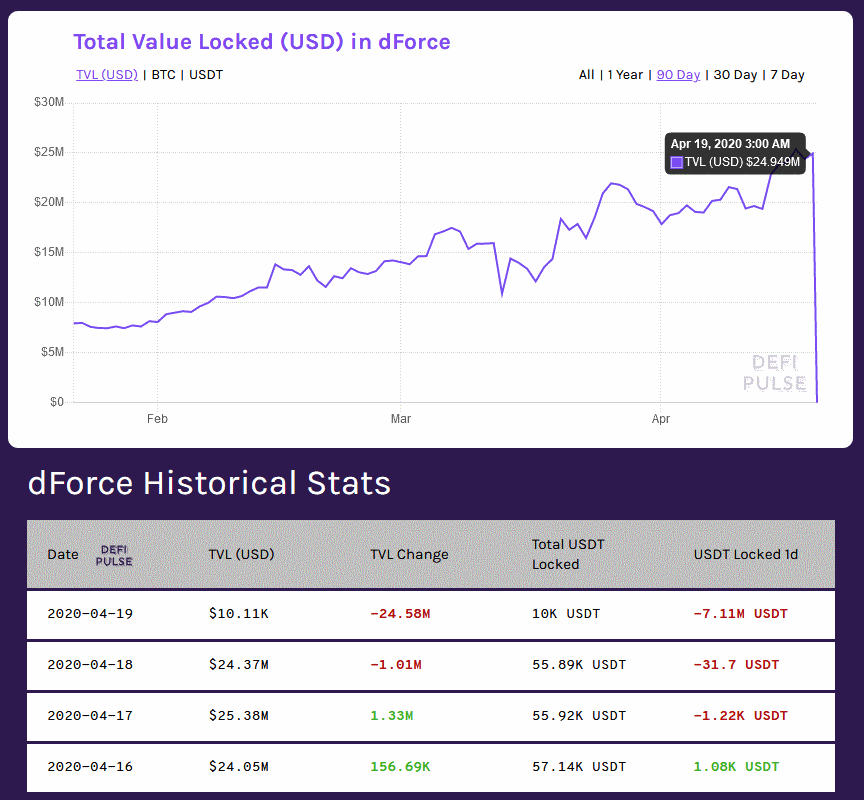
At the time of writing, Uniswap is believed to have lost between $300,000 and $1.1 million in funds, while Lendf.me lost more than $24.5 million.